Artificial urinary sphincter
It is a device that is implanted in the patient to allow him/her to control the sphincter manually avoiding urine leaks.

What is the artificial urinary sphincter?
The urinary sphincter is a muscle that allows the body to hold back urine. Normally, the sphincter remains contracted until the person decides to relax it to urinate. When a person has difficulty controlling the urinary sphincter, he or she may have involuntary urine leakage.
When this happens, the implantation of an artificial urinary sphincter is a second-line treatment to end stress urinary incontinence. It is recommended in cases where incontinence is severe or when placement of a mesh or sling has not solved the problem.
It is a long-term, durable solution for female urinary incontinence and male urinary incontinence, but for its implantation it is important that the patient is able to manually control the device. The physician will perform an examination to ensure that there are no contraindications to its placement.
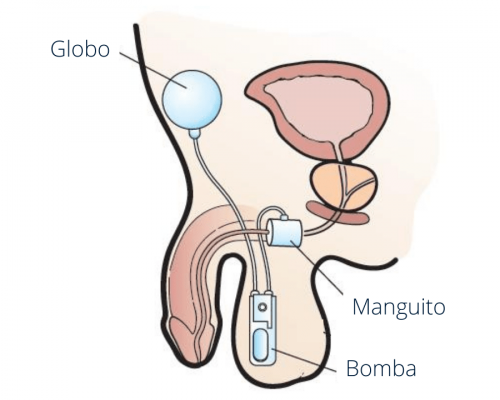
The artificial urinary sphincter consists of three parts:
- A cuff. This is a silicone ring that fits around the urethra. When the cuff inflates (fills with fluid), it puts pressure on the urethra and contracts it to block the passage of urine. When you need to urinate, the cuff deflates (empties of fluid) and reduces pressure on the urethra to allow urine to flow out.
- A balloon, which contains a small amount of saline solution and regulates the cuff pressure. The liquid is displaced into it when the cuff is deflated.
- A pump, which causes the fluid to enter or exit the cuff. In the case of women, the pump mechanism is placed in the lips of the vulva and in the case of men, in the scrotum.
To use the artificial sphincter when a patient wants to urinate, he/she must squeeze the pump placed on the scrotum (in the case of a man) or labia vulvae (in the case of a woman). The pump causes fluid to flow out of the cuff and into the balloon, allowing the cuff to deflate and the urethra to open. The cuff remains open for one minute for urination. It then closes automatically.
What does the artificial urinary sphincter operation consist of?
For the implantation of the artificial urinary sphincter in men, the surgeon will make two small incisions under general or epidural anesthesia: one in the scrotum, where he will place the cuff, and another near the lower abdomen. In women, the approach is usually laparoscopic or abdominal.
When the surgery is finished, the incisions will be closed with sutures (stitches) that will dissolve on their own without the need to remove them.
After the operation, the patient will remain hospitalized for 24 hours with a catheter to drain the urine. After this time, the patient will be discharged with a series of recommendations described by the urologist.
The artificial urinary sphincter will not be activated for approximately six weeks, when it has healed completely. Therefore, the patient will continue to have urinary incontinence during this time. During this period, you may also experience pain in the pelvic area or pain when urinating. Your doctor may prescribe medication to alleviate these symptoms.
During the first week after your surgery, your urologist may recommend that you wear a scrotal jockstrap and wait six weeks before you begin strenuous activities such as exercising at the gym, riding a bike or lifting more than 10 pounds. Your doctor will tell you when you can resume sexual activity.
- Results maintained over time
- Return to daily activities in a few days avoiding major efforts
- No longer need to use absorbent diapers
- Need to avoid physical exertion during the first weeks after surgery.
- Complete study prior to surgery that may limit surgical treatment to be indicated in all patients.
- Need to learn how to use the device
Our team has years of experience in the treatment of severe urinary incontinence in both men and women. We perform a detailed study of our patients in order to assess the most appropriate treatment.
The professionals of our service receive patients with complex incontinence situations evaluated in other centers for surgical management. In addition, we work together with pelvic floor physiotherapists to optimize results and perform the first step of treatment.
Our experience and activity is registered in the European Association of Urology (EAU), being listed as the professionals with the highest surgical activity in this regard in our country. In addition, the registration in international databases allows us to audit the results and compare them with other centers of excellence.
+20
years of experience
We are the professionals with the highest surgical activity in our country.
We receive patients with complex incontinence situations assessed in other centers for surgical management.
Newsof ROC Clinic in Artificial urinary sphincter
Research
Current management of stage T1 renal cell carcinoma in Spain: Results of a multicenter national registry.
They ask us in the Consultation
See more questionsTeam of the Artificial Urinary Sphincter Unit


 +34 912 627 104
+34 912 627 104 Contact
Contact












