Benign Prostate Hyperplasia

- Super-specialized urologists
- Personalized treatment
- Minimally invasive approach
- More than 16,000 patients successfully treated
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is the enlargement of the prostate gland which, because of its anatomical position, results in obstruction of the outflow of urine from the bladder. It is a common condition that affects men as they age.
This growth is not cancerous or related to prostate cancer, but it can interfere with the normal flow of urine by compressing the urethra. Although it is a benign process, its progression can significantly impact quality of life if not properly treated.
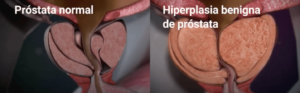
Benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostatic enlargement manifests itself mainly after the age of 40. At this age, 40% of men present symptoms of this disease, which are mainly manifested in alterations in urinary dynamics. This percentage increases by 10% as each decade progresses, so that almost all men over 80 years of age have urinary problems.
At ROC Clinic, we have a team specialized in the integral approach to BPH, offering personalized solutions and minimally invasive technologies that allow us to treat this condition safely, effectively and with rapid recovery.
They ask us in the Consultation
Is benign prostatic hyperplasia dangerous?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is not a cancer nor does it increase the risk of developing it, therefore, it is not a dangerous disease in itself. However, if not treated properly, it can lead to major complications that do seriously affect health and quality of life. Among the possible consequences of uncontrolled BPH are: acute urinary retention (inability to urinate), recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder stone formation, progressive damage to the bladder or kidneys. Therefore, although it is not malignant, it does require medical attention and urological follow-up. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, BPH can be effectively controlled and complications avoided.
Does prostate hyperplasia surgery cause sexual problems? Is it very aggressive?
Not at all. In recent years we have more and more technology that allows us to perform minimally invasive prostate surgery without causing sexual side effects.
Since I have prostate problems I have sexual problems... is it related?
Yes, very much so. Prostate problems can lead to impotence and premature ejaculation. That's why sometimes early treatment of prostate hyperplasia can prevent you from developing sexual problems.
Should I follow any diet to take care of my prostate?
It is good to drink at least 2 liters of water a day and avoid foods high in saturated fats, condiments, spices and pepper. It is also advisable to reduce the intake of coffee and alcohol, especially white drinks and beer.
Team of the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Unit
Newsof ROC Clinic on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Research
Initial experience with thulium fiber laser for prostate enucleation: Analysis of the intraoperative and short-term outcomes in a prospective, multicenter cohort.
Treatments
ROC Clinic has performed more than 3,000 prostate enucleation procedures with Holmium laser.
Training
Programming of the 2022 courses in Holmium laser prostatic enucleation.


 +34 912 627 104
+34 912 627 104 Contact
Contact














